Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(5):1198-1206. doi:10.7150/ijms.50039 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Risk factors for mortality of critically ill patients with COVID-19 receiving invasive ventilation
1. Department of Anesthesiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
3. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
Abstract
Rationale: Early invasive ventilation may improve outcomes for critically ill patients with COVID-19. The objective of this study is to explore risk factors for 28-day mortality of COVID-19 patients receiving invasive ventilation.
Methods: 74 consecutive adult invasively ventilated COVID-19 patients were included in this retrospective study. The demographic and clinical data were compared between survivors and non-survivors, and Cox regression analysis was used to explore risk factors for 28-day mortality. The primary outcome was 28-day mortality after initiation of invasive ventilation. Secondary outcome was the time from admission to intubation.
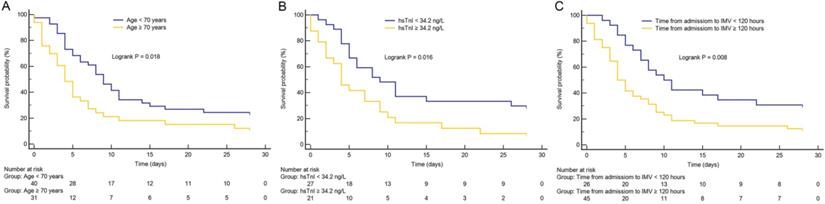
Results: Of 74 patients with COVID-19, the median age was 68.0 years, 53 (71.6%) were male, 47 (63.5%) had comorbidities with hypertension, and diabetes commonly presented. The most frequent symptoms were fever and dyspnea. The median time from hospital admission to intubation was similar in survivors and non-survivors (6.5 days vs. 5.0 days). The 28-day mortality was 81.1%. High Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score (hazard ratio [HR], 1.54; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.23-1.92; p < 0.001) and longer time from hospital admission to intubation (HR, 2.41; 95% CI, 1.15-5.07; p = 0.020) were associated with 28-day mortality in invasively ventilated COVID-19 patients.
Conclusions: The mortality of invasively ventilated COVID-19 patients was particularly striking. Patients with high SOFA score and receiving delayed invasive ventilation were at high risk of mortality.
Keywords: COVID-19, critically ill, mortality, risk factor, invasive ventilation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact