3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(5):1121-1129. doi:10.7150/ijms.51594 This issue Cite
Review
Environmental Pollution and Chronic Kidney Disease
1. Department of Family Medicine, Kaohsiung Municipal Ta-Tung Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
2. Department of Family Medicine, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
3. Graduate Institute of Clinical Medicine, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
4. Research Center for Environmental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
5. Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
6. Department of Internal Medicine, Kaohsiung Municipal Siaogang Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
7. Faculty of Medicine, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
Abstract
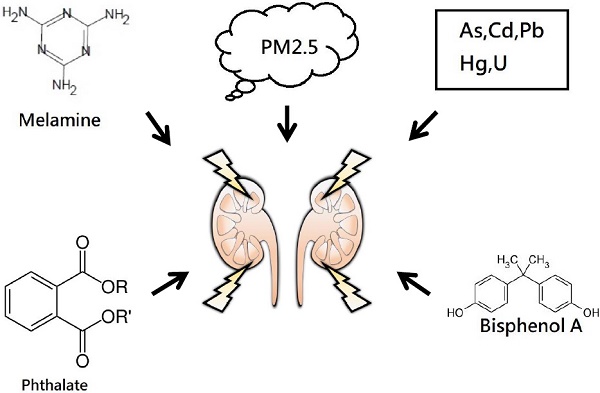
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a global public health problem associated with high rates of morbidity and mortality due to end-stage renal disease and cardiovascular disease. Safe and effective medications to reverse or stabilize renal function in patients with CKD are lacking, and hence it is important to identify modifiable risk factors associated with worsening kidney function. Environmental pollutants, including metals, air pollutant, phthalate and melamine can potentially increase the risk of CKD or accelerate its progression. In this review, we discuss the epidemiological evidence for the association between environmental pollution and kidney disease, including heavy metals, air pollution and other environmental nephrotoxicants in the general population.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease, environmental pollution, heavy metal

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact