3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(1):29-41. doi:10.7150/ijms.49728 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Longitudinal clinical and radiographic evaluation reveals interleukin-6 as an indicator of persistent pulmonary injury in COVID-19
1. Guangzhou Eighth People's Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China
2. Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
* Baolin Liao, Zhipeng Liu, Libo Tang, Linghua Li, and Qingxin Gan are co-first authors
# Yaling Shi, Yongyin Li, and Chunliang Lei contributed equally.
Abstract
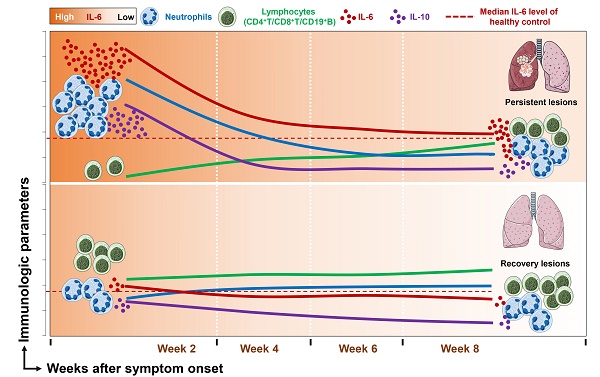
Rationale: Previous studies of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) were mainly focused on cross-sectional analysis. In this study, we sought to evaluate the dynamic changes of immunological and radiographic features, and the association with the outcome of pulmonary lesions in COVID-19 patients.
Methods: Peripheral blood samples and radiographic data were collected longitudinally for up to 8 weeks from 158 laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patients. The chest computed tomography (CT) scans were scored based on a semi-quantification assessment according to the extent of pulmonary abnormalities; the temporal change of the immunological and radiographic features was analyzed.
Results: Compared with mild and moderate patients, severe patients had significantly decreased counts of lymphocytes, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and CD19+ B cells but dramatically elevated counts of neutrophils and levels of interleukin (IL)-6. Sequential monitoring showed a sustained increase in lymphocytes counts and significantly decreased levels of IL-6 in severe patients during the disease course. Notably, patients with persistent pulmonary lesions (CT score ≥ 5 in week 8) showed high levels of IL-6 during the follow-up period, compared with those with recovery lesions (CT score < 5 in week 8). More importantly, the peak expression of IL-6 prior to the aggravated lung injury was mainly found in patients with persistent lesions, and multivariate analysis showed that IL-6 level upon admission was an independent factor associated with the persistent pulmonary injury.
Conclusion: Prolonged elevation of IL-6 is associated with persistent pulmonary lesions in COVID-19 patients. Sequential monitoring and timely intervention of IL-6 may favor the clinical management of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19, interleukin-6, pulmonary injury, chest CT, sequential monitoring

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact