ISSN: 1449-1907International Journal of Medical Sciences
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(5):848-861. doi:10.7150/ijms.89490 This issue Cite
Review
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS): State of the Art and Future Directions
1. Department of Medicine and Medical Specialities, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Alcalá, 28801 Alcalá de Henares, Spain.
2. Ramón y Cajal Institute of Sanitary Research (IRYCIS), 28034 Madrid, Spain.
3. Department of Public and Maternal and Child Health, School of Medicine, Complutense University of Madrid, 28040 Madrid, Spain.
4. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University Hospital Gregorio Marañón, 28009 Madrid, Spain.
5. Health Research Institute Gregorio Marañón, 28009 Madrid, Spain.
6. Department of Surgery, Medical and Social Sciences, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Alcalá, 28801 Alcala de Henares, Spain.
7. Department of General and Digestive Surgery, University Hospital Príncipe de Asturias, 28805 Madrid, Spain.
8. Department of Nursing and Physiotherapy, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Alcalá, Alcalá de Henares, Spain.
9. Service of Pediatric, Hospital Universitario Principe de Asturias, 28801 Alcalá de Henares, Spain.
10. Pathological Anatomy Service, Central University Hospital of Defence-UAH Madrid, 28801 Alcala de Henares, Spain.
11. Immune System Diseases-Rheumatology and Internal Medicine Service, University Hospital Príncipe de Asturias, CIBEREHD, 28806 Alcalá de Henares, Spain.
Abstract
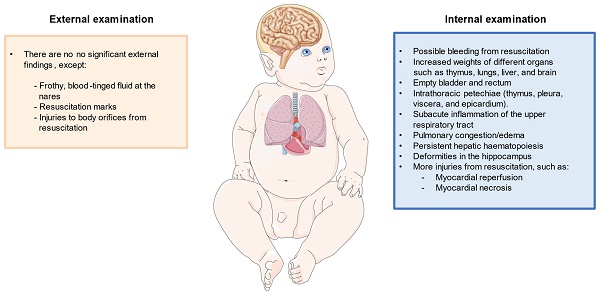
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) is a type of death that occurs suddenly and without any apparent explanation, affecting infants between 28 days of life and up to a year. Recognition of this entity includes performing an autopsy to determine if there is another explanation for the event and performing both an external and internal examination of the different tissues to search for possible histopathological findings. Despite the relative success of awareness campaigns and the implementation of prevention measures, SIDS still represents one of the leading causes of death among infants worldwide. In addition, although the development of different techniques has made it possible to make significant progress in the characterization of the etiopathogenic mechanisms underlying SIDS, there are still many unknowns to be resolved in this regard and the integrative consideration of this syndrome represents an enormous challenge to face both from a point of view scientific and medical view as humanitarian. For all these reasons, this paper aims to summarize the most relevant current knowledge of SIDS, exploring from the base the characterization and recognition of this condition, its forensic findings, its risk factors, and the main prevention measures to be implemented. Likewise, an attempt will be made to analyze the causes and pathological mechanisms associated with SIDS, as well as potential approaches and future paths that must be followed to reduce the impact of this condition.
Keywords: sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), forensic findings, risk factors, preventive measures, etiopathogenesis
