ISSN: 1449-1907International Journal of Medical Sciences
Int J Med Sci 2024; 21(4):612-622. doi:10.7150/ijms.88476 This issue Cite
Review
Ferroptosis: A New Mechanism in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
1. Department of Geriatrics, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, China.
2. Department of Neurology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430000, China.
Abstract
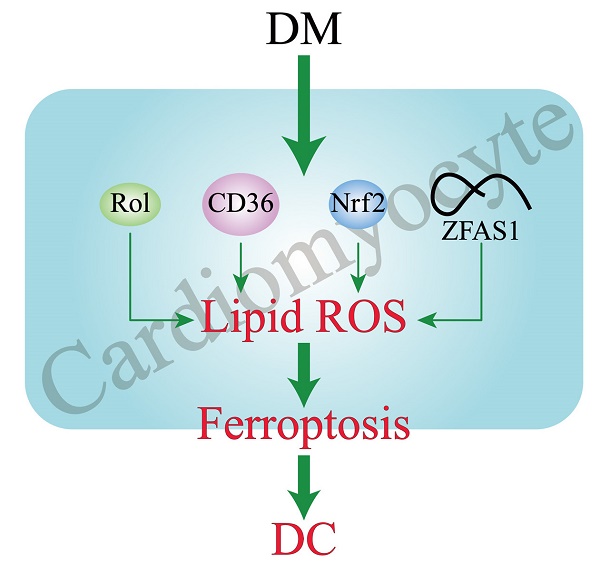
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DC) is a pathophysiologic condition caused by diabetes mellitus (DM) in the absence of coronary artery disease, valvular heart disease, and hypertension that can lead to heart failure (HF), manifesting itself in the early stages with left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction, with marked HF and decreased systolic function in the later stages. There is still a lack of direct evidence to prove the exact existence of DC. Ferroptosis is a novel form of cell death characterized by reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and lipid peroxidation. Several cell and animal studies have shown that ferroptosis is closely related to DC progression. This review systematically summarizes the related pathogenic mechanisms of ferroptosis in DC, including the reduction of cardiac RDH10 induced ferroptosis in DC cardiomyocytes which mediated by retinol metabolism disorders; CD36 overexpression caused lipid deposition and decreased GPX4 expression in DC cardiomyocytes, leading to the development of ferroptosis; Nrf2 mediated iron overload and lipid peroxidation in DC cardiomyocytes and promoted ferroptosis; lncRNA-ZFAS1 as a ceRNA, combined with miR-150-5p to inhibit CCND2 expression in DC cardiomyocytes, thereby triggering ferroptosis.
Keywords: Diabetic cardiomyopathy, Ferroptosis, Mechanism
